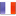
Hepatic steatosis (also called fatty liver disease) is the accumulation of fat in the liver. When inflammation is present, the condition is called steatohepatitis and can progress to cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). It is one of the most common liver diseases and consists of excess fat that is deposited in the liver cells, making them malfunctioning. This condition is reversible and can be treated with a healthy lifestyle through natural or medicinal treatments including herbal preparations and also with natural dietary supplements.
 There are two types of steatosis: non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis and alcoholic hepatic steatosis. Non-alcoholic Liver steatosis is a syndrome that develops in non-alcoholic patients due to the diet rich in saturated fats. Most often occurs in middle-aged women, overweight persons, persons with diabetes or with an elevated triglycerides in the blood. Initially, most patients do not have symptoms. However, fatigue, general feelings of illness and pain in the chest are some of the symptoms. Alcoholic steatohepatitis is a consequence of alcohol abuse for a long period of time. The symptomatology is similar to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
There are two types of steatosis: non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis and alcoholic hepatic steatosis. Non-alcoholic Liver steatosis is a syndrome that develops in non-alcoholic patients due to the diet rich in saturated fats. Most often occurs in middle-aged women, overweight persons, persons with diabetes or with an elevated triglycerides in the blood. Initially, most patients do not have symptoms. However, fatigue, general feelings of illness and pain in the chest are some of the symptoms. Alcoholic steatohepatitis is a consequence of alcohol abuse for a long period of time. The symptomatology is similar to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Liver steatosis without complications is reversible, so it is necessary to apply a treatment to protect the liver. In case where hepatic steatosis is caused by food, it is recommended to avoid fatty meat, animal fats, where as, the patient diet should mostly contain vegetables, fruits, fiber, whole grains, brown rice, mushrooms. If hepatic steatosis is caused due to chronic alcoholism, then avoiding the alcohol consumption is essential for the treatment and leads to regression of the disease. For chronic smokers, it is essential to stop smoking.
Non-alcoholic liver steatosis liver disease is reversible. Thus, a healthy lifestyle is essential in the treatment of non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis. The patient must have a balanced diet, avoiding medicaments that are not absolutely necessary, avoid alcohol and tobacco. Maintaining blood sugar levels (for diabetics), progressive decrease in weight (in case of obesity), lowering cholesterol and treatment prescribed by a doctor are particularly important factors in the treatment of non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis.
The causes leading to hepatic steatosis:
The most common causes that can lead to hepatic steatosis include: alcohol abuse (risk of the disease is dependent on the amount and duration of alcohol consumption), high-fat diet, obesity, diabetes, genetic disorders, bowel resection, a number of drugs (such as some contraceptives), dyslipidemia (elevated levels of cholesterol and / or triglycerides in the blood), presence of hepatitis C virus, rapid changes in weight (both rapid growth and loss of weight), pregnancy, toxic substances, etc.
Hepatic steatosis – Symptoms:
Hepatic steatosis is usually asymptomatic. However, some people have fatigue, weakness or pain in the right subcostal region of the body. The later stage liver disease is characterized by symptoms such as jaundice or ascites (fluid in the peritoneal cavity). Following clinical examination, the doctor may also discover hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver).
Hepatic steatosis and diet:
Hepatic steatosis is considered a reversible condition, so it is recommended to undergo a liver protection therapy. In both cases of steatosis it is recommended to avoid drinking alcohol.
In case of hepatic steatosis caused by diet, it is recommended not to eat animal fats, fatty meat, the diet of the patient must be predominant in fruits, vegetables, cold pressed oils, whole grains, fiber, mushrooms, foods with vitamin C. In the case of hepatic steatosis due to alcoholism, it is necessary to give up alcohol completely, along with a change in diet, which leads to rapid regression of the disease. Body weight should be within normal limits, so overweight persons are recommended for a weight loss therapy. It is also important to expel all toxins which are accumulated in the body, hence substances such as tobacco and consumption of alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Also, in the treatment of hepatic steatosis, the patient must comply sleep hours, also recommended to avoid stress and should carry out sports activities for at least 30 minutes every day.
Experts of STAR INTERNATIONAL MED created product LIVECOM Syrup, a natural protector of the liver. It is a natural dietary supplement of ayurvedic herbs with tonic, regenerating, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulant, antioxidant and antitumor properties that contributes to the health of the body by improving liver functions and activities. LIVECOM syrup helps purify the liver, spleen and blood by expelling toxins accumulated due to excess consumption of alcohol, drugs and medications causing hepatotoxicity as adverse effect.
LIVECOM syrup is a natural dietary supplement effective in case of hepatic steatosis, protects the liver cell degeneration, contributes to its natural regeneration, thus ensuring the proper metabolism of food. LIVECOM syrup helps the body to recover after food poisoning, hepatotoxic medication and remedies in cases of hepatic steatosis. Helps maintain the health of the liver, spleen and blood, contributes to mitigate the effects of acute and chronic hepatic inflammatory conditions, protects the liver cell, to maintain the general tone of the body during recovery from weakness due to its revitalizing effect of its herbs content.
Herbs contained in LIVECOM syrup include: Picrorrhiza kurroa (Kutki), Terminalia chebula (Haritaki), Andrographis paniculata (Kalmegh), Boerhaavia diffusa (Punarnava), Eclipta alba (Bhringaraj), Phyllanthus urinaria (Bhumyamalaki), Tinospora cordifolia (Guduchi), Emblica officinalis (Amla), Tecoma undulata (Roheda), Fumaria officinalis (Fumitory), Silybum marianum (Milk thistle), Aloe barbadensis (Aloe). Herbs contained in this product are eficient in hepatic disorders, as well as in case of hepatic steatosis.
Picrorrhiza kurroa (Kutki) is a herb which is found in Himalayan regions of Kashmir and Sikkim, at an altitude of 2700-4500 meters. Its bioactive ingredients have strong detoxifying properties, being recommended in cases of jaundice, viral hepatitis, hepatotoxicity, alcoholism, hepatic steatosis, anorexia, hepatomegaly, asthma, dysapnoea, cough, cold, dermatological problems, intestinal worms, menorragia, urinary system disorders, etc.
Terminalia chebula (Haritaki) is a tree having its origin in South Asia, India to Nepal, in Yunnam regions of China, in southern zones of Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Vietnam. Terminalia Chebula is a medicinal herb used in case of various liver disorders and in bowel diseases. It has strong antioxidant, hepatoprotector, antibacterial, antiviral, anticarcinogenic, radioprotector, cardioprotective, adaptogen, antianaphyllactic, hypolipidemic, hypocholesterolemic and antiulcer properties.
Eclipta alba (Bhringaraj) is an exceptional herb in hepatic disorders. It is beneficial in case of hepatic steatosis due to its strong hepatoprotector, antimicrobial, antiinflammatory, analgezic properties. It is a good liver tonic with imunostimulant and rejuvenanting properties.
Emblica officinalis (Amla) is considered in Ayurveda as Rasayana (rejuvenator) and used specially in case of degenerative processes of the body. Including the fact that it has strong beneficial effects on the body, it is recommended and used in various diseases such as: diabetes, colics, flatulence, peptic ulcer, hepatic steatosis, hepatopathy, jaundice, diarrhea, hemorrhage, leucorrhea, menorrhagia, skin diseases, dispepsia, bronchial asthma, etc.
Silybum marianum (Milk thistle) herb contains silymarin as its principal ingredient. It is frequently recommended in cases of hepatic steatosis. Silymarin contained in this herb has strong hepatoprotector, antifibrosis, antioxidant benefits, as well as it is a strong detoxifier and regenerator of liver cells.