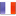
The digestive system represents a group of morphological and functional organs that help in digestion and absorption of ingested food and help to expel undigested or nonassimilated food. The main functions of digestive system are to provide necessary nutrients to the body cells, which is performed through digestion and absorption process. The foods we consume are vital, containing essential nutrients like: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, water, vitamins and minerals. All substances present in foods are utilized by the body, which absorbs the assimilable nutrients out of them. The role of digestive system consists of converting food to monosaccharides, fatty acids and amino acids which are to be assimilated.
Digestion begins in the oral cavity and most of the process takes place in the intestine, not in the stomach which we tempted to believe. Teeth begin the process of degradation of food by mechanical action. Salivary glands impregnate the fregmented food with saliva. Saliva contains an enzyme, ptyalin, which plays an initiator role of carbohydrate digestion. Crushed and masticated food is transformed into a paste. This “food dough” is then swallowed, passing through the pharynx and slided down through esophagus, then reaches in the stomach by an involuntary mechanism.
Once the food reaches inside the stomach, it is then mixed with gastric juice, which contains a significant amount of hydrochloric acid (helps in destroying bacteria) and activates the enzyme called pepsinogen, which is converted into pepsin and breaks down long chained food proteins. In the stomach, food undergoes various changes that allow its subsequent absorption by the small intestine. Small contractions of muscle layers are generated approximately from 20 to 20 seconds, allowing mixing of food with secretions and the semifluid mass of partly digested food called “chime” expelled by the stomach into the duodenum through a sphincter called the pyloric sphincter.
Digestion in the small intestine is continued by reducing the level of simple sugars carbohydrates, lipids in monoglycerides and fatty acids, proteins in amino acids or peptides. For this, the small intestine needs bile and pancreatic secretions (pancreatic secretion is rich in enzymes help in the digestion of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids, while biliary secretion plays an important role in digestion of lipids). Absorbtion of transformed food substances is carried out by enterocytes (intestinal cells that allow the passage of food into the bloodstream) in each segment of small intestine. Iron, calcium and vitamins are absorbed preferentially in the duodenum. Carbohydrates and fats are absorbed in the duodenum and jejunum and bile salts in the ileum. Materials that have not been absorbed are pushed towards large intestine through the peristaltic movements. Digestion in colon relies on a microbial degradation without much utility for nutrition. Nutrients absorbed through intestine, enter to the bloodstream, because they might be processed by vital organs and finally distributed to cells.
As a result of poor nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, abdominal discomfort may occur. Bacteria in the intestinal flora, located mainly in the colon decompose food residues through two main mechanisms: fermentation and putrefaction. The decomposition results gas and toxin accumulation and irritation occures when putrefaction mechanism predominates. When intestinal flora imbalance occurs (as a result of unbalanced and disordered eating, consumption of alcohol or antibiotics), it results in slowing down transit followed by modifying digestion processes leading to the feeling of heaviness in the stomach. Unpleasant events like flatulence (bloating) and belching (belching) may also occur. In the case of a slow intestinal transit, toxins produced by waste residue remaining for too much time in intestine and can be absorbed into the body. Also, intestine “stores” waste of eaten food for several days, and in this situation, the feeling of heaviness in the stomach occurs. When food transits in digestive tube between 48-72 hours duration, we may consider it a slow intestinal transit and if the duration is more than 72 hours, then we can consider it as constipation.
For digestive system health, specialists of STAR INTERNATIONAL MED have created Ayurmed brand (a brand of STAR INTERNATIONAL MED) ayurvedic remedies GASCURE Tablets and GASCURE Syrup.
Nausea
Nausea (described as the sensation of vomiting), whether or not vomiting, is a feeling to the body intolerance tolerate about something or problems with sense of smell or equilibrium. The center which stimulates this reaction, as well as that of vomiting is located in the brain. Often imminent vomiting is asociated by a feeling of exhaustion in the stomach, sweating, salivation, decreased blood pressure and heart rate, dizziness and tremors. Face of the person turns pale, sometimes headaches and restlessness with panic sensation also occur. Nausea is an “anxiety” of the stomach that often accompanies the urge to vomit but not always lead to vomiting instead, represents a forced, voluntary or involuntary emptying of stomach contents through mouth.
Nausea often precedes vomiting, occurred as an isolated symptom, it may reveal a heart attack, kidney, liver, central nervous system disorder, brain tumors and some other forms of cancer. Often, nausea is one of the ways of body’s defense after excessive consumption of food or alcohol, contaminated foods and intoxication with chemical substances.
Nausea and motion sickness, various diseases, early pregnancy, intense pain, emotional stress, gallbladder disease, different types of viruses, certain odors or flavors are some of the causes of nausea and vomiting. The causes of vomiting differ according to age. For example, in adults, vomiting is usually the result of a viral infection and/or food poisoning whereas in children, vomiting occurs due to a viral infection, food poisoning, motion sickness, overeating, coughing and due to the disease in which the child has a high fever. One major problem associated with vomiting is dehydration. Adults have a lower risk of dehydrated than children. To prevent nausea, there are certain recommendation which could be followed easily like eating food slowly with proper mastication to avoid bloating and nausea after eating, avoid too copious foods/meals, cooking food in a proper manner (means it should be well cooked/fried/roasted), ensuring good hygiene conditions while keeping the food in kitchen, refrigerator and during food preparation to prevent food poisoning. After an episode of vomiting, it is advisable to eat easily digestible foods like: rice, simple or creamy soups, yogurt, mashed potatoes, bananas. Avoid fatty foods, coffee, tea or alcohol. Also, hydration plays an important role. Some herbal remedies indicated consuming for existing nausea/vomiting are ginger, cinnamon, chamomile, anise, mint, etc.
In case of nausea/vomiting STAR INTERNATIONAL MED’s specialists have created an ayurvedic remedy made from herb extracts, GASCURE Tablets.
Indigestion
Indigestion occurs after a copious meal or after eating contaminated food and is more common in people who have problems with stomach, liver or pancreas. It has a higher frequency in summer, when food can spoil more quickly. Also, stress, excessive alcohol and tobacco contribute to slow digestion. Statistics show that 50% of adults suffer at least once in a month with indigestion.
Indigestion, also called dyspepsia medically, can have many causes and can be accompanied by other symptoms (feeling satiety during or after eating, pain in the upper abdomen and burning sensation in the upper abdomen, nausea, bloating, belching, hiccups, diarrhea etc). In most of the times indigestion occurs suddenly and does not last longer. There are some people who suffer from chronic indigestion Foods that are not completely digested get fermented and causes a bitter taste in the mouth, abdominal colics, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea and fever.
Among the most common causes of indigestion are spicy foods, fast-food, rapid eating habits, carbonated beverages, acute or chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, some medicaments (excessive consumption of antibiotics, medicaments containing acetyl slicylic acid, etc.). In terms of Ayurveda, indigestion is a result of excessive accumulation of “Ama” (toxins) in the stomach, decreased digestive fire (metabolism) “Agni” (represented by totality of digestive enzymes).
If the indigestion symptoms occur at night, it is recommended not to eat 3 hours before bedtime. Also, use several pillows to sleep with head elevated to prevent entry of gastric acid to the esophagus. When you know that you are going to take a gourmet meal with copious preparations, it is always good to have a fresh pineapple in the refrigerator. Shortly after the meal, eat 1-2 slices of pineapple which helps improve digestion due to its bromelain content, a digestive enzyme. Kiwi fruit has the same effect. Mint, saffron, ginger and fennel seeds are among some Ayurvedic remedies useful in case of indigestion.
In case of indigestion STAR INTERNATIONAL MED’s specialists have created a natural ayurvedic remedy made from herb extracts, GASCURE Tablets.
Ayurveda And Intestinal Parasitosis
Various diseases caused by intestinal parasites have an important place in human pathology and knowledge of their manifestations is absolutely necessary in the current conditions. Intestinal parasites appear due to unhealthy diet that creates propitious environment for their growth and multiplication. If not treated in time, this problem can seriously affect the health of people.
Intestinal parasitosis is a digestive disorder, commonly seen in both children (except breast feeding infants, which do not have any chance of direct contamination and have negligible incidence of intestinal parasites in early months of life), in adults and elderly. It is caused by worms or parasites (non vertebrate species, without legs, elongated, soft-bodied and usually bearing a glossy skin and live in soil, water or as parasites on herbs and animals). The most common species are: Giardia lamblia, pinworms, ascaris, tapeworm, toxoplasmosis, etc. Intestinal parasites are often caused by poor hygiene, contaminated water sources or infected animals. These may affect your health by releasing toxins and by using all the nutritional resources inside the body.
Parasites reach in the digestive system by swallowing or inhalation of contaminated food (contaminated meat, insufficiently cooked, unwashed vegetables and contaminated water) and contact of the body with animals already having parasites. Intestinal parasites can survive in the digestive tract for years without causing any symptoms.
Headache, weakness, constipation, diarrhea, stools with blood, bloating, vomiting, abdominal pain are some of the symptoms associated with intestinal parasitosis. Intestinal parasites can enter the body in many ways, and their mechanism of action is different from one to another. The most common way of parasite manifestation is that of food and water contaminated with parasites, eggs and larvae. Some eggs and larva of the parasites can not be destroyed by gastric acid and intestinal secretion and are capable to survive in the intestine, which favors as a suitable environment for their development and multiplication.
The symptomatology in children is well defined and more illustrative, whereas in adults, the symptoms are more discreet, associated mainly with moderate nervous and digestive system manifestations (nervousness, fatigue, malaise, abdominal pain, bowel problems, halitosis or bad breath from mouth, excessive hunger, etc). Diagnosis is performed following coproparasitologic exam (three exams in total, at an interval of 2 days).
In Ayurveda, parasites treated with a triple approach, which is based on both the removal the cause, and “recovery” of the affected portions: restoring intestinal flora affected by parasites, detoxify the liver and blood due to the release of toxins and changes pH caused by parasites. Measures to prevent and combat intestinal parasites and general hygienic are: proper hygiene, room ventilation, lavatory sanitation, keeping food in strict hygiene conditions, washing fruits and vegetables before their consumption, proper hand wash and nail cutting.
For intestinal parasites STAR INTERNATIONAL MED’s specialists have created a natural ayurvedic remedy made from herb extracts, WORM END Syrup.
Gastritis
If you have pain in stomach, accompanied by burning sensation which does not let you enjoy your favorite foods, then you may suffer from gastritis. Gastritis is a common disorder of the digestive system which, if remain untreated or treated superficially, can be dangerous due to its irreversible complications. Gastritis represents inflammation of the gastric mucosa by inflammatory, degenerative or metaplastic processes. These mucosal lesions may progress towards healing, with a self-limiting nature, or on the contrary, may be evolving to serious complications with gastric bleeding, ulceration with peritonitis or high risk of degeneration in adenocarcinoma (stomach cancer).
As a classification, gastritis can be acute or chronic and according to symptoms, gastritis can be classified as per clinical point of view as symptomatic or asymptomatic. Copious meals and fatty foods which are difficult to digest affect gastric mucosa. Other factors that cause gastritis are chronic administration of medicines, such as aspirin, excessive consumption of alcohol and spicy preparations, infectious factors (viral hepatitis, herpes, bacterial toxinfections, infection with Helicobacter pylori, candida, etc). The symptomatology of gastritis is often unspectacular, with dull and tolerable pain, which does not have periodicity, regularity, appearing every now and then, and with evolution of the disease, occurs more frequently and gets more intense.
Acute gastritis is one of the most common forms of gastritis, which is characterized by reversible superficial or deep inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Acute gastritis occurs as a direct effect of internal factors (reflux of bile from the duodenum into the stomach, especially after some surgical interventions) or external factors (abuse of alcohol, spicy foods and foods which are hard to digest, etc). The term “acute” reflects the speed and time of evolving the disease. This form of gastritis may develop within days or even in hours. If remain untreated, acute gastritis can become chronic, leading to severe complications. Catarrhal gastritis is the mild and most common form of acute gastritis. It is characterized by superficial inflammation of gastric mucosa. Typically, catarrhal gastritis develops with in several hours (after food poisoning) and disappears in a few days without special treatment.
Erosive gastritis is characterized by appearance of ulcers (erosions) on the surface of the gastric mucosa. Depending on the severity of the disease, ulcers may be superficial (mild) or deep (severe form). In some cases of acute gastritis, deep erosion can cause bleeding (hemorrhage), in these cases, the disease is called “hemorrhagic gastritis.” Gastric mucosa is swollen by edema and congestion and erosion bleeding occurs at the mucosal surface and even acute ulcers. Acute ulcer heals quickly and has no tendency to relapse, but should not be confused with chronic ulcers.
Phlegmonous gastritis is a rather rare but extremely dangerous acute gastritis. It is characterized by suppurative inflammation followed by damaging the mucosal wall. This form of gastritis is specific to people with weakened immune systems. Phlegmonous gastritis symptoms may include fever, vomiting and severe abdominal pain. If these symptoms appear then they needed specialist medical attention. Without proper treatment, phlegmonous gastritis usually leads to death.
From clinical point of view, acute gastritis can be “silent”, without any manifestation, but there is a presence of endoscopical lesions, even severe and may occur suddenly with upper gastrointestinal bleeding without pain or even with pain, nausea, bloating, vomiting, epigastric pain (in the chest) of variable intensity, which usually occur after spicy meals or meals which are hard to digest. Chronic gastritis is a fairly common form of gastritis, is characterized by long term gastric inflammation, usually over 6 months. This form of gastritis develops over many years and causes irreversible disorder of the structure and function of the stomach. Gastric inflammation undergoes a superficial form, then the person feels better, pain alleviates for a while and an apparent recovery occurs in gastric mucosa, but it does not fully recover. Chronic gastritis persists if causal factors persist: infection with Helicobacter pylori, chronic alcohol consumption, eating unhealthy fast food, etc. When Gastric mucosa suffers from atrophy, with no acid secretion and becomes nonfunctioning, it may lead to a serious cause of stomach cancer.
The clinical signs of chronic gastritis are characterized by feelings of pressure and epigastric burning, permanent dull pain, sometimes with dorsal irradiation that can be influenced mainly by the change of position or movement. Epigastric pain intensity is variable, with no fixed schedule and uncertain evolution. Pain usually occurs after having spicy-sour meals, after consuming alcohol in excess, due to indigestible foods and also, is accompanied by pyrosis (burning sensation ascends from the stomach through the esophagus with a sour taste associated with hyperacidity) and flatulence.
Diet is very important in case of gastritis. Human body has a natural tendency to increase seasonal gastric acidity, especially during spring and autumn. Therefore gastritis symptoms occur especially in those seasons. Avoid fried, sour, excessively spicy foods, soups and meat soups (which increase gastric acidity), fruits and uncooked vegetables which are harder to digest and their digestion requires prolonged stagnation in the stomach, followed by increased gastric acid secretion. Avoid concentrated sweets (such as honey, jam, candy, chocolate), cream, animal fats, dry beans, cabbage, fast food, carbonated, alcoholic and caffeinated beverages. Also, specialists recommend eating less at meals but at multiple times, so that there will always be something in the stomach to “buffer” the acid. Along with that avoid eating too cold or too hot meals.
Natural herb remedies are also available to alleviate gastric problems. Ayurmed brand natural ayurvedic natural dietary supplement GASCURE Tablets, stimulates gastric and hepatobiliary secretions, alleviating discomforts caused by overeating, alleviating nausea, thus contributing to the proper functioning of digestion and intestinal absorption. Protects gastric mucosa, regulates bowel, is an adjuvant in case of oral candidiasis and provides antioxidant benefits. Can be administered both in adults and children over 5 years of age.
Gastric hyperacidity crises manifested by burning sensations in the stomach, acid regurgitation in esophagus and inefficient digestion can be tackled easily with the help of Ayurmed brand natural dietary supplement GASCURE Syrup. It acts gently on gastric glands, protecting the gastric mucosa by acting as a balm on existing gastric lesions, stops their further expansion, helps restore affected gastric and intestinal epithelium. At the same time, GASCURE syrup regulates gastric and hepatobiliary secretion and provides a normalizing effect on digestion.
Gastric And Duodenal Ulcer
An ulcer is a crater-like sore in the gastric mucosa or duodenum (the first part of the intestine). Ulcer disease can be occured at any age, but young people have maximum chances of occurance. These injuries occur when gastric secretions containing hydrochloric acid and an enzyme called pepsin irritate and damage the gastric mucosa. These Gastric secretions can affect the esophagus also. Peptic ulcers in the gastric mucosa are called gastric ulcers whereas those occurring in duodenal mucosa are called duodenal ulcers. Gastric and duodenal ulcers are caused by the presence of the potential acidic environment of the stomach.
Ulcer represents an interruption in a protective gastric mucosa, surrounding the digestive tract which is the result of dysfunction of the stomach’s defense mechanisms (mucus and bicarbonate) and harmful actions of external and intrinsic factors, which lead to increase the secretion of pepsin, gastrin and hydrochloric acid. The most common clinical manifestation of ulcer is pain. However, in 10% to 40% cases, ulcers evolve as asymptomatic, means without pain. A few years ago it was believed that eating spicy food and stress may cause ulcers, but today it is demonstrated that administration of anti-inflammatory drugs (eg aspirin) and Helicobacter pylori infection are also the main causes. Helicobacter pylori present in 50-70% of people diagnosed with gastric ulcer and present in 30-50% of those who diagnosed with duodenal ulcer. But not all people who are infected with H. pylori develop peptic ulcer disease. Also, smoking is a risk factor depending on the number of cigarette smoked per day. Cigarette smoking decreases strength of healing and increases the incidence of relapses.
Although stress is a causative factor of ulcers, it aggravates its manifestations and sometimes delays healing. Treatment, irrespective of preventive or curative, dietetic or medicinal in acute and chronic phases of ulcers, seeks control of gastric acid and gastric mucosal strengthening.
For your digestive tract health STAR INTERNATIONAL MED’s specialists have created a natural Ayurvedic remedy made from herb extracts, GASCURE Syrup.